Media
Newspaper and News Agencies
![The first edition of the Dongnipsinmun, [The Independent]. Launched on April 7, 1896, it was Korea's first privately-owned all-Hangeul newspaper](http://www.korea.net/cheditor40_asp/cheditor/attach/200852717563961106.jpg)
The first edition of the Dongnipsinmun, [The Independent]. Launched on April 7, 1896, it was Korea's first privately-owned all-Hangeul newspaper
Over the following decades, Korean newspapers found their greatest challenge in upholding the nationalistic spirit of the Korean people and opening their eyes to the rapidly changing world. The newspapers played an important role in independence movements during the Japanese colonial regime (1910-1945).
The Chosun Ilbo and the Dong-A Ilbo are the two oldest newspapers in Korea, both inaugurated in 1920 in the wake of the March First Independence Movement. Both newspapers are known for their independent editorial policies and considerable influence on public opinion. This spirit persisted through the establishment of the Republic of Korea in 1948. With broad leeway to criticize officialdom, newspapers have always been at the forefront of leading social changes.
Korean newspapers have made significant investments in modern press facilities and equipment in recent years. Most national dailies operate computerized typesetting and editing systems with multicolor printing capability.
There are two major news agencies in Korea, Yonhap News and Newsis. With an extensive news-gathering network in the capital city and provinces, Yonhap News also maintains 23 overseas bureaus in Europe, North America, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and South America. And Newsis, which was registered in 2001, has provided news services since June 2002.
Television

TV home networking demonstration
In December 1961, KBS-TV was inaugurated by the government as the first full-scale television service in Korea. Another broadcast firm, TBC-TV, began operation in December 1964. The Munhwa Broadcasting Corporation established Korea's third television station, MBC-TV, in August 1969. During a period of media mergers in the late 1980s, TBC-TV was taken over by KBS and renamed as KBS-2.
EBS (the Educational Broadcasting System), under the supervision of the Ministry of Education, started broadcasting in 1990. EBS broadcasts extracurricular educational programs for students and also cultural programs and documentaries. EBS became a public corporation under the new Broadcasting Law in June 2000.
SBS (the Seoul Broadcasting System) began broadcasting under private management in 1990. The first privately-operated local stations ― PSB (Busan Broadcasting Corp.), TBC (Daegu Broadcasting Corp.), KBC (Gwangju Broadcasting Company) and TJB (Daejeon Broadcasting Corp.) ― were established in 1995 to promote local culture and spur regional development. A second group of privately-operated local stations ― iTV (Incheon Television Corp.), UBC (Ulsan Broadcasting Corp.), CJB (Cheongju Broadcasting Corp.) and JTV (Jeonju Television Corp.) ― began operating in 1997. Some of the broadcasters have discontinued their operations, while others have been renamed.
![Korea Multimedia phone: LG Electronics' mobile phone with a DMB [Direct Multimedia Broadcasting] function](http://www.korea.net/cheditor40_asp/cheditor/attach/200852917185624460.jpg)
Korea Multimedia phone: LG Electronics' mobile phone with a DMB [Direct Multimedia Broadcasting] function
The KBS, MBC, SBS and EBS television networks launched digital broadcasting in the Seoul metropolitan area in the latter half of 2001. The service was expanded to the greater Seoul and surrounding areas in 2002.
Cable TV was first introduced in Korea in 1970. It was popular mainly among those who could not enjoy good TV reception due to geographical conditions or man-made structures.
However, since the late 1980s, as public demand for more information and a greater variety of entertainment increased, demand for cable TV has also been on the increase.
Cable TV started experimental services in 1990. As of the end of 2005, 14.0 million subscribers were able to view about 70 cable channels broadcasting programs for 77 subject areas.
Korea has put three telecommunications satellites ― Mugunghwa Nos. 1, 2, 3 ― into orbit since 1995 and secured 168 satellite channels to broadcast programs in such diverse areas as sports, music, education and entertainment. Korea Digital Broadcasting (KDB) launched a satellite broadcasting service in March 2002, and as of the end of 2004, it was providing diverse channel services to about 1.65 million subscribers. The satellites also paved the way for Korea to become one of the leading nations in information technology.
Radio

Studio of Bae Chul-soo's Music Camp, MBC's pop music program
This was the only radio station in the country until 1954, when the Christian Broadcasting System (CBS), operated chiefly with contributions from churches, started educational and religious programming along with news and entertainment broadcasts.
In December 1956, another Christian organization, the Evangelical Alliance Mission, inaugurated the Far East Broadcasting Station in Incheon, and the first commercial radio enterprise in Korea, the Busan Munhwa Broadcasting Station, was established in Busan in April, 1959. The founding of several private broadcasting companies followed. MBC (Munhwa Broadcasting Company) began operations in December 1961 with the call sign KLKV, followed by two rivals, DBS (Dong-A Broadcasting Station) in 1963 and TBC (Dongyang Broadcasting Company) in 1964.
Another wave of change took place in 1990 with the establishment of a number of specialized broadcasting stations.
Korea's global English-language cable network Arirang TV
The Seoul city-operated TBS (Traffic Broadcasting Station) was set up in June, 1990, followed by the government-operated EBS (Educational Broadcasting Station). Pyeonghwa Broadcasting Corporation (PBC) for Catholics and the Buddhist Broadcasting System (BBS) were also established in 1990.
In March 1991, the privately-owned Seoul Radio Station began broadcasting to a target audience among the Seoul Metropolitan area and its vicinity, while five other privately-owned local FM radio channels opened in 1997.
There are presently a total of 202 radio broadcasters in the Republic of Korea; 153 FM, 47 AM, and two shortwave services for Koreans overseas. Despite the increasing popularity of television, radio still has an expanding audience in Korea.
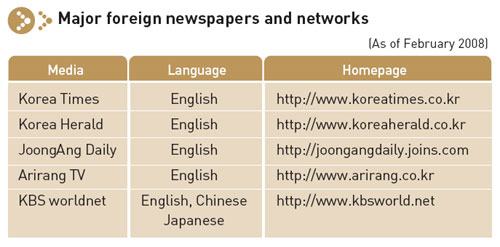
|
|